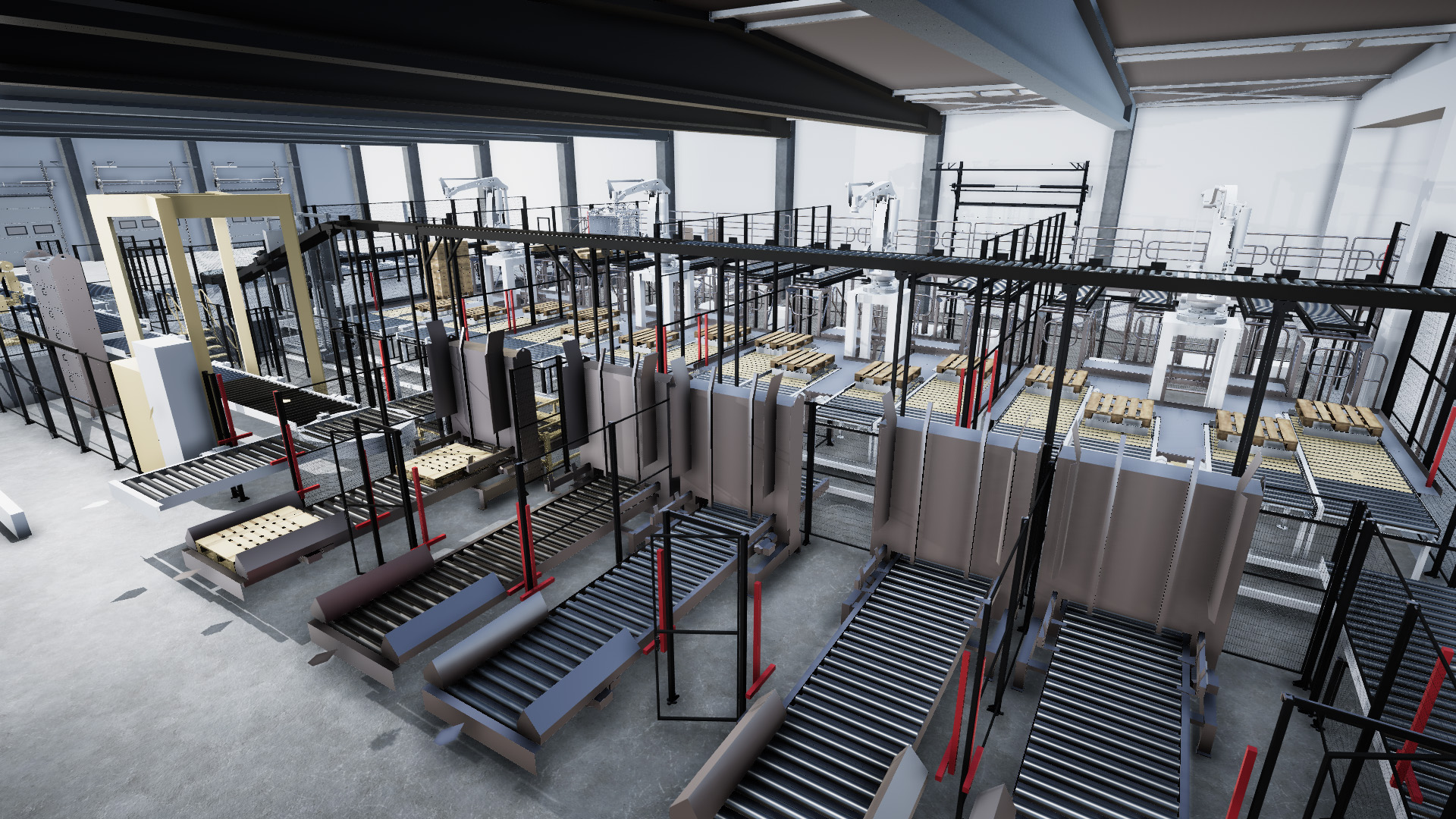


What Are Digital Twins and How Are They Revolutionizing Smart Manufacturing?
Digital twins have emerged as a game-changing technology in the realm of smart manufacturing. But what exactly are digital twins, and why are they garnering so much attention? In simple terms, a digital twin is a virtual replica or simulation of a physical asset, process, or system. By integrating real-time data and advanced analytics, digital twins enable manufacturers to gain unparalleled insights, optimize operations, and enhance decision-making capabilities.
How Do Digital Twins Benefit Smart Manufacturing?
Digital twins offer numerous advantages in smart manufacturing and are revolutionizing traditional industrial practices. Firstly, they provide a comprehensive understanding of a physical asset’s behaviour, performance, and maintenance requirements. Manufacturers can monitor real-time data from their digital twins, enabling predictive maintenance and minimizing downtime. Furthermore, digital twins facilitate simulation and testing of new product designs, leading to faster development cycles and reduced costs. The ability to optimize processes and identify inefficiencies in real-time allows for continuous improvement and increased productivity. With these benefits in mind, it’s no wonder that digital twins are gaining traction across industries
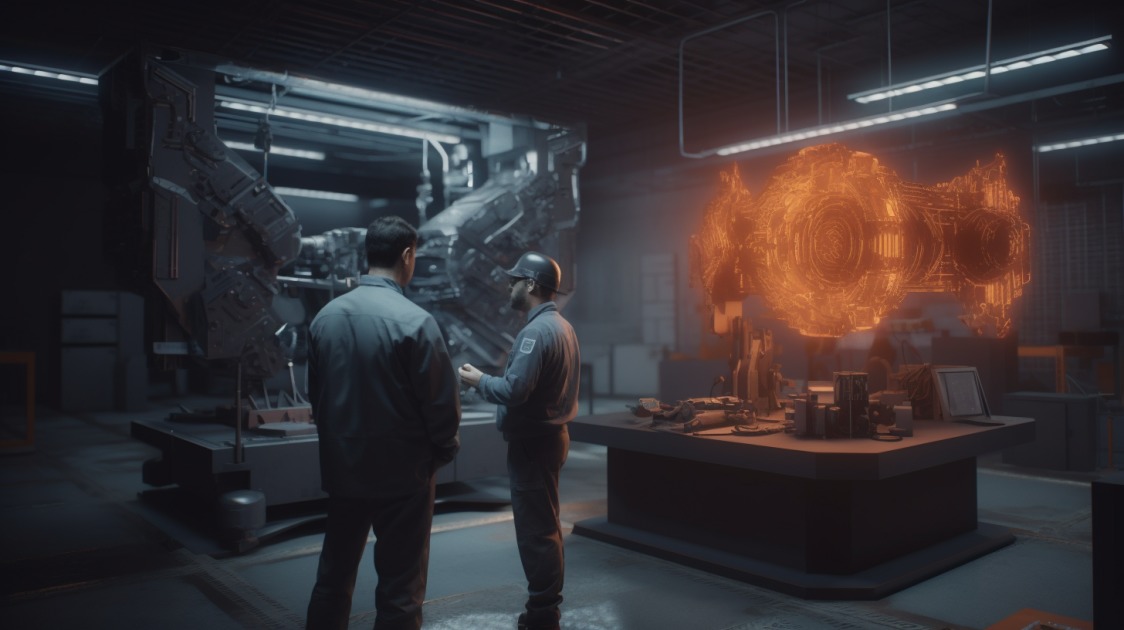

How Are Digital Twins Practically Used in Smart Manufacturing?
Digital twins find practical applications across the entire manufacturing lifecycle, from product development to ongoing operations. During the design phase, engineers can create virtual models of products or production lines and simulate their behaviour. This helps in identifying design flaws, optimizing performance, and ensuring product quality before physical prototypes are even built. Once in operation, digital twins continuously gather data from sensors embedded in the physical assets. This data can be used to monitor performance, detect anomalies, and optimize operations in real-time. By coupling real-time insights with advanced analytics, manufacturers can make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
How are Digital Twins created?
The first step in creating a digital twin is to model the 3d geometry of the building. This can come from existing 3D models or, if none exist, by using 3D laser scanning to capture the environment in 3D. Luminous use the latest mobile mapping technology to provide rapid data capture with minimal disruption and requiring zero production down time. Scan data is hosted online in a collaborative portal called Ivion. Scan data is then converted by our modelling team into asbuilt 3D geometry. The geometry is just the start or ‘Digital Model’, the next phase is to imbue the digital twin with real time data from the actual factory to create a ‘Digital Shadow’.
This is done by tapping into existing sensor information or retro fitting old analogue machines to create digital outputs which send data to the 3D model. To do this, Luminous create the 3D model from the laser scans and then build a real-time interactive environment in the Unity games engine. Once this environment is connected to live sensor data engineers and analysts can begin to run virtual simulations, training scenarios or even virtual meetings.
The final and more challenging step is to create a true ‘Digital Twin’ where not only is external sensor data being fed into the 3D environment, but actions carried out or data generated in the digital twin is fed back to the real world creating a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement.
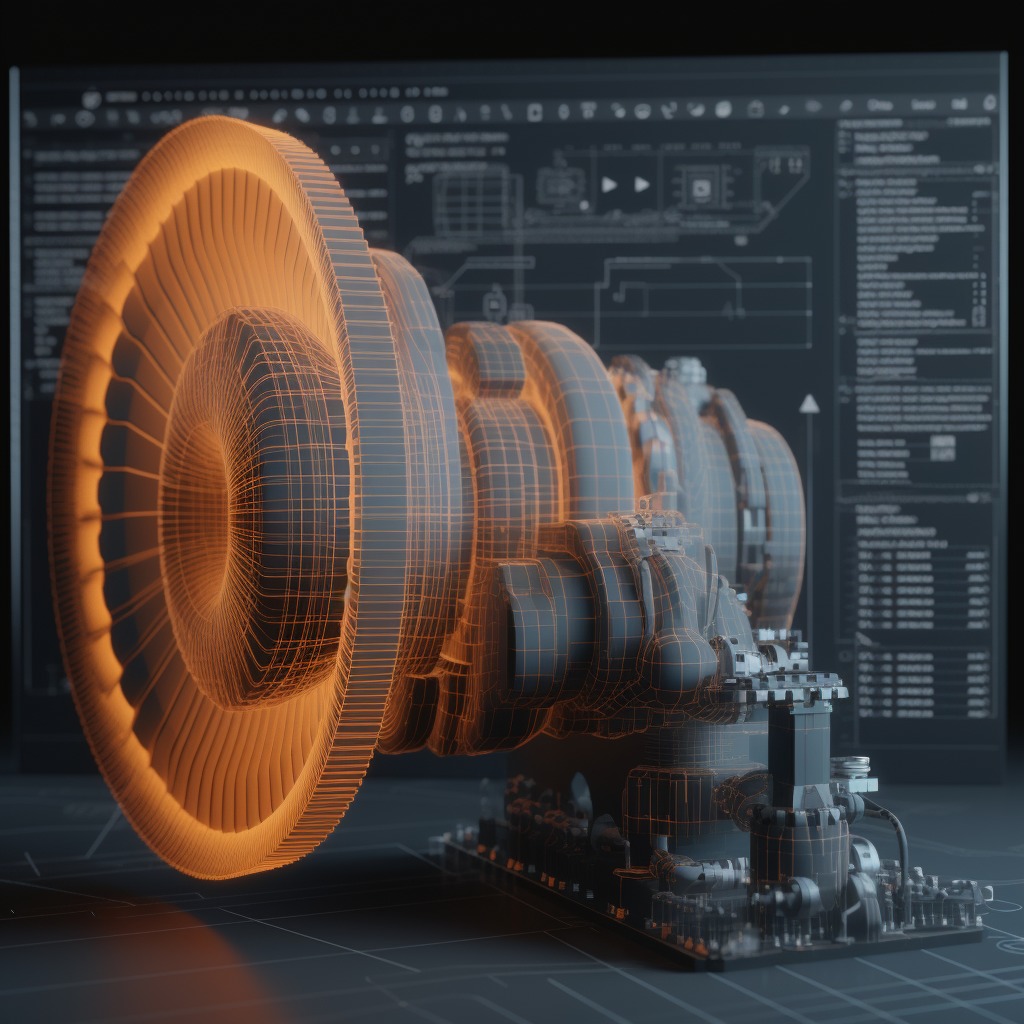
How Are Digital Twins Practically Used in Smart Manufacturing?
Digital twins find practical applications across the entire manufacturing lifecycle, from product development to ongoing operations. During the design phase, engineers can create virtual models of products or production lines and simulate their behaviour. This helps in identifying design flaws, optimizing performance, and ensuring product quality before physical prototypes are even built. Once in operation, digital twins continuously gather data from sensors embedded in the physical assets. This data can be used to monitor performance, detect anomalies, and optimize operations in real-time. By coupling real-time insights with advanced analytics, manufacturers can make data-driven decisions to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer satisfaction.
How are Digital Twins created?
The first step in creating a digital twin is to model the 3d geometry of the building. This can come from existing 3D models or, if none exist, by using 3D laser scanning to capture the environment in 3D. Luminous use the latest mobile mapping technology to provide rapid data capture with minimal disruption and requiring zero production down time. Scan data is hosted online in a collaborative portal called Ivion. Scan data is then converted by our modelling team into asbuilt 3D geometry. The geometry is just the start or ‘Digital Model’, the next phase is to imbue the digital twin with real time data from the actual factory to create a ‘Digital Shadow’.
This is done by tapping into existing sensor information or retro fitting old analogue machines to create digital outputs which send data to the 3D model. To do this, Luminous create the 3D model from the laser scans and then build a real-time interactive environment in the Unity games engine. Once this environment is connected to live sensor data engineers and analysts can begin to run virtual simulations, training scenarios or even virtual meetings.
The final and more challenging step is to create a true ‘Digital Twin’ where not only is external sensor data being fed into the 3D environment, but actions carried out or data generated in the digital twin is fed back to the real world creating a virtuous cycle of continuous improvement.

Embracing the Digital Twin Revolution in Smart Manufacturing
As the fourth industrial revolution takes hold, digital twins are emerging as a key technology driving the transformation of smart manufacturing. The ability to create virtual replicas of physical assets and systems empowers manufacturers with real-time insights, predictive capabilities, and enhanced decision-making abilities. From optimizing product designs to streamlining operations, digital twins have revolutionized traditional industrial practices. By leveraging this technology, companies can unlock new opportunities for innovation, improved efficiency, and sustainable growth. As we move forward, the adoption of digital twins in smart manufacturing will likely continue to rise, reshaping the industry landscape and propelling manufacturers towards a more connected and intelligent future.